Top 10 Drugs that Causes Kidney Damage
Table of Contents
Top 10 Drugs that Causes Kidney Damage
Are you aware that some of the medicines you take may harm your kidneys? Kidneys are vital organs in our body responsible for filtering wastes and toxins from our blood. However, certain drugs can cause damage to these important organs that could lead to kidney failure or other complications. In this blog post, we will discuss the top 10 drugs that cause kidney damage and how they affect the functions of our kidneys. Whether you’re taking prescription medications or over-the-counter drugs, it’s essential to know which ones may be harmful to your kidneys’ health!
1. Diuretics
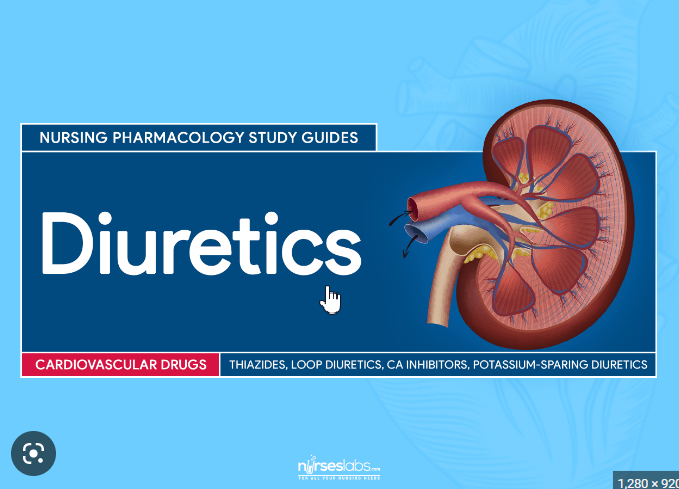 Diuretics are commonly prescribed medications used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and other conditions related to fluid retention. They work by increasing urine production and reducing the amount of water in your body. While diuretics can be beneficial for some patients, they may also cause kidney damage if not taken properly.
Diuretics are commonly prescribed medications used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and other conditions related to fluid retention. They work by increasing urine production and reducing the amount of water in your body. While diuretics can be beneficial for some patients, they may also cause kidney damage if not taken properly.
One type of diuretic called loop diuretics is known to cause kidney damage when used at high doses or for a prolonged period. These drugs act on the kidneys’ tubules, which can lead to electrolyte imbalances that affect renal function. Thiazide diuretics are another type of drug that can cause kidney problems with long-term use. They work by blocking sodium reabsorption in the kidneys but may also decrease potassium levels in the body, leading to complications such as muscle weakness and cramps.
If you’re taking diuretics long-term or notice any unusual symptoms like decreased urine output or swelling around your ankles and feet, it’s best to consult your doctor immediately. They will monitor your condition closely and adjust your medication dose accordingly while minimizing potential risks for kidney damage.
2. Laxatives
 Laxatives are commonly used for relieving constipation and promoting bowel movements. However, prolonged use of laxatives can cause kidney damage. These drugs work by stimulating the muscles in the intestines to contract and move stool out of the body. Some types of laxatives work by drawing water into the intestine, making stool soft and easier to pass. This can lead to dehydration if not enough fluids are consumed while taking these medications.
Laxatives are commonly used for relieving constipation and promoting bowel movements. However, prolonged use of laxatives can cause kidney damage. These drugs work by stimulating the muscles in the intestines to contract and move stool out of the body. Some types of laxatives work by drawing water into the intestine, making stool soft and easier to pass. This can lead to dehydration if not enough fluids are consumed while taking these medications.
Another type of laxative called sodium phosphate can cause kidney injury if taken in high doses or over a long period of time. It is important to follow dosing instructions carefully when using any type of laxative. People with underlying kidney problems should be particularly cautious when taking laxatives as they may worsen their condition. In some cases, alternative treatments such as dietary changes or exercise may be more appropriate. If you experience any symptoms such as decreased urine output or swelling in your hands or feet while taking a laxative, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider right away.
3. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
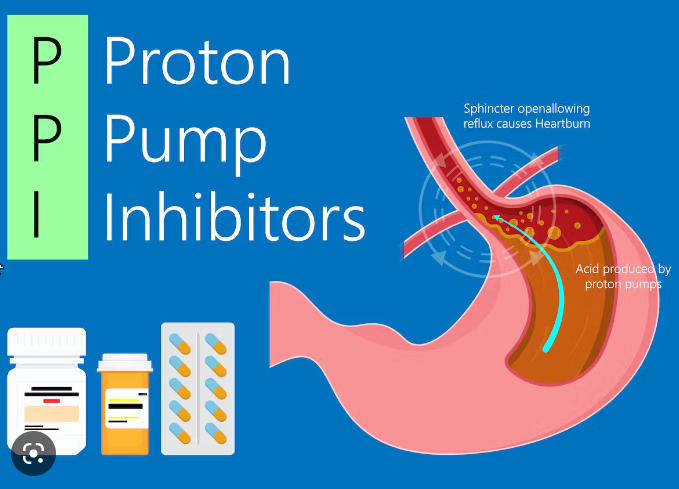 Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) are a type of medication commonly used to treat acid reflux and heartburn. While they can be effective in reducing symptoms, prolonged use of PPIs has been linked to kidney damage. Studies have shown that taking high doses of PPIs for an extended period of time can increase the risk of chronic kidney disease. This is because these medications reduce the body’s ability to absorb calcium, which is essential for healthy bones and kidneys.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) are a type of medication commonly used to treat acid reflux and heartburn. While they can be effective in reducing symptoms, prolonged use of PPIs has been linked to kidney damage. Studies have shown that taking high doses of PPIs for an extended period of time can increase the risk of chronic kidney disease. This is because these medications reduce the body’s ability to absorb calcium, which is essential for healthy bones and kidneys.
In addition, long-term use of PPIs can cause inflammation and damage to the lining of the kidneys, leading to decreased kidney function over time. It’s important for individuals taking PPIs to monitor their kidney function regularly through blood tests and speak with their healthcare provider if they notice any changes or symptoms. Alternative treatments such as lifestyle changes or alternative medications may be recommended by healthcare providers for those who experience acid reflux and heartburn symptoms without risking further harm on their kidneys.
4. Jardiance
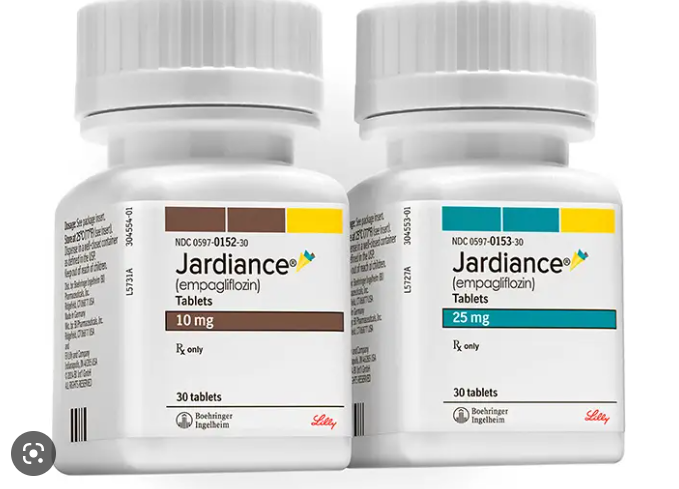 Jardiance is a medication that belongs to the class of drugs known as SGLT2 inhibitors. It is commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes by lowering blood sugar levels in the body. One study revealed that patients taking Jardiance had a higher risk of developing ketoacidosis, which is a condition where there are high levels of ketones in the blood. This can lead to severe dehydration and affect kidney function.
Jardiance is a medication that belongs to the class of drugs known as SGLT2 inhibitors. It is commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes by lowering blood sugar levels in the body. One study revealed that patients taking Jardiance had a higher risk of developing ketoacidosis, which is a condition where there are high levels of ketones in the blood. This can lead to severe dehydration and affect kidney function.
Jardiance also increases the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) due to its diuretic effect. UTIs can lead to bacterial infections in the kidneys if left untreated, causing damage over time. It is important for individuals who take Jardiance or any other medication for type 2 diabetes to regularly monitor their kidney function through regular check-ups with their doctor. If you experience any symptoms such as swelling or pain in your lower back or sides, difficulty urinating or changes in urine colour, seek medical attention immediately.
In summary, while Jardiance may be an effective medication for managing type 2 diabetes, it should be taken with caution due to its potential effects on renal function and increased risk of UTIs.
5. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
 Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to manage pain and inflammation. However, prolonged use of NSAIDs can cause damage to the kidneys. These drugs work by blocking enzymes that produce prostaglandins, which are responsible for causing pain and inflammation in the body.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to manage pain and inflammation. However, prolonged use of NSAIDs can cause damage to the kidneys. These drugs work by blocking enzymes that produce prostaglandins, which are responsible for causing pain and inflammation in the body.
The risk of developing kidney damage from NSAIDs is higher in people with pre-existing kidney disease or those who take high doses of these drugs regularly. Symptoms of kidney problems include swelling in the legs and feet, decreased urine output, fatigue, nausea and vomiting. It’s important for patients taking NSAIDs on a regular basis to talk to their healthcare provider about monitoring their kidney function through blood tests. In some cases, alternative medications may be recommended or adjustments made to dosage amounts.
Ultimately, it’s crucial for individuals taking any kind of medication – especially long-term – to understand its potential effects on overall health and communicate with healthcare professionals when concerns arise.
6. Zoledronic acid
 Zoledronic acid is a medication used to treat high levels of calcium in the blood caused by cancer. It works by slowing down the breakdown of bone, which can release calcium into the bloodstream. However, like many other drugs, Zoledronic acid has been linked with kidney damage. The drug is eliminated from the body through urine and excessive use or prolonged use of this medication can lead to renal dysfunction.
Zoledronic acid is a medication used to treat high levels of calcium in the blood caused by cancer. It works by slowing down the breakdown of bone, which can release calcium into the bloodstream. However, like many other drugs, Zoledronic acid has been linked with kidney damage. The drug is eliminated from the body through urine and excessive use or prolonged use of this medication can lead to renal dysfunction.
If you’re currently taking Zoledronic acid or any other medication that might affect your kidneys, it’s important to speak with your doctor about potential risks and ways to protect yourself from further harm. By being aware of these risks and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can help safeguard your health while continuing to receive effective treatment for cancer-related conditions.
7. Foscarnet
 Foscarnet is a medication that is used to treat viral infections, particularly those caused by herpes viruses. While it can be effective in treating these conditions, foscarnet has been known to have some serious side effects on the kidneys. When taking foscarnet, patients need to be monitored closely for any signs of kidney damage or impairment. This includes regular blood tests and urine samples to check for changes in kidney function. If left unchecked, kidney damage caused by foscarnet can lead to more severe complications such as chronic kidney disease.
Foscarnet is a medication that is used to treat viral infections, particularly those caused by herpes viruses. While it can be effective in treating these conditions, foscarnet has been known to have some serious side effects on the kidneys. When taking foscarnet, patients need to be monitored closely for any signs of kidney damage or impairment. This includes regular blood tests and urine samples to check for changes in kidney function. If left unchecked, kidney damage caused by foscarnet can lead to more severe complications such as chronic kidney disease.
It’s important for healthcare providers and patients alike to weigh the potential benefits of using foscarnet against the risks associated with this drug. In some cases, alternative treatments may be available that do not carry the same risk of kidney damage. If you are prescribed foscarnet or any other medication that could potentially harm your kidneys, make sure you understand all of the possible risks involved before starting treatment. And if you experience any unusual symptoms while taking this drug or others like it – such as decreased urine output or swelling in your legs or feet – seek medical attention right away to get checked out for potential kidney issues.
8. Aminoglycoside antibiotics
 Aminoglycoside antibiotics are a class of drugs that are commonly used to treat bacterial infections. They work by interfering with the bacteria’s ability to produce proteins, which ultimately leads to their death.
Aminoglycoside antibiotics are a class of drugs that are commonly used to treat bacterial infections. They work by interfering with the bacteria’s ability to produce proteins, which ultimately leads to their death.
Although they can be effective in treating certain infections, aminoglycosides have been known to cause kidney damage in some patients. This is because these drugs are eliminated from the body through the kidneys, and high doses or prolonged use can lead to irreversible kidney damage. One of the most common side effects of aminoglycoside antibiotics is decreased urine output, which may indicate that the kidneys are not functioning properly. Other symptoms include swelling in the legs or ankles, fatigue, and difficulty breathing.
Patients who have pre-existing kidney disease or who take other medications that can affect renal function should be closely monitored if they require treatment with aminoglycosides. In some cases, doctors may need to adjust the dosage or switch to an alternative medication altogether.
9. Vancomycin
 Vancomycin is a potent antibiotic used to treat severe infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria. It works by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis, thereby preventing the growth and spread of harmful microorganisms in the body. Although Vancomycin is effective in treating serious infections such as endocarditis, meningitis, and pneumonia, it can also cause kidney damage if not properly administered. This drug should be given at appropriate doses for a specific duration of time to prevent toxicity.
Vancomycin is a potent antibiotic used to treat severe infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria. It works by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis, thereby preventing the growth and spread of harmful microorganisms in the body. Although Vancomycin is effective in treating serious infections such as endocarditis, meningitis, and pneumonia, it can also cause kidney damage if not properly administered. This drug should be given at appropriate doses for a specific duration of time to prevent toxicity.
Vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity occurs when the kidneys are unable to filter out waste products from the blood effectively. Symptoms include decreased urine output or changes in its colour, fatigue, shortness of breath, swelling in extremities and high blood pressure. Patients who are already suffering from impaired renal function need to avoid taking this medicine altogether because they may develop acute kidney injury. Hence healthcare providers must monitor patients’ kidney function regularly during treatment with Vancomycin.
1o. HIV medications and antiviral drugs
 HIV medications and antiviral drugs are essential for managing HIV infection, but they can also cause damage to the kidneys. These medications work by slowing down the replication of the virus in the body, which helps prevent further damage to the immune system. While HIV medications and antiviral drugs are critical for managing HIV infections effectively; they should always be taken under close medical supervision due to their potential side effects on kidneys health. People living with this condition must understand how vital it is always not overlooking any signs indicating possible complications that could arise from taking these medicines long term without proper care or consultation from medical professionals
HIV medications and antiviral drugs are essential for managing HIV infection, but they can also cause damage to the kidneys. These medications work by slowing down the replication of the virus in the body, which helps prevent further damage to the immune system. While HIV medications and antiviral drugs are critical for managing HIV infections effectively; they should always be taken under close medical supervision due to their potential side effects on kidneys health. People living with this condition must understand how vital it is always not overlooking any signs indicating possible complications that could arise from taking these medicines long term without proper care or consultation from medical professionals
It is important to be aware of the various drugs that can cause kidney damage. While some medications may be necessary for certain medical conditions, it’s crucial to talk with your doctor about any potential side effects or risks before starting a new medication.
If you are taking any of the above-listed medications and experience symptoms such as decreased urine output, swelling in your legs or ankles, fatigue, nausea or shortness of breath, seek immediate medical attention. Remember to always follow your doctor’s instructions when taking medication, and never adjust dosages without consulting them first. By being informed and proactive about your health care choices, you can help protect yourself from potential kidney damage caused by prescription drugs.